Unified Auditing
Oracle Database provides the industry’s most comprehensive auditing capability with Unified Auditing, a feature that captures the most accurate record of any database activity. Unified Auditing provides a single, unified audit trail for all audit records, simplifying the management and analysis of audited data. With it, you can monitor and detect suspicious database activities while better managing your compliance requirements.
- What’s new in Database 23ai for database audit?
Oracle Database 23ai introduces a new ability to audit access to certain columns in tables and views. It enables you create more narrowly targeted audit policies that reduce "noise" from unnecessary audit records.
- Build simple and effective audit policies
Learn to provision more precise unified audit policies that are targeted to your corporate and compliance needs.
- 2025 KuppingerCole Leadership Compass for Data Security Platforms
Discover why KuppingerCole recognized Oracle as a Leader in database security.
Benefits of Unified Auditing
-
Accelerate regulatory compliance
Documented records of user activity provide assurance to regulatory authorities that data is used only in intended ways.
-
Detect anomalous database access
Recognizing abnormal database activities early on means you can act quickly to correct the security threat and minimize damage.
-
Enable forensics
A centralized and simplified audit trail provides a wealth of accurate information on data access that is useful for forensic investigations.
Explore Unified Auditing use cases
Monitor privileged user activity
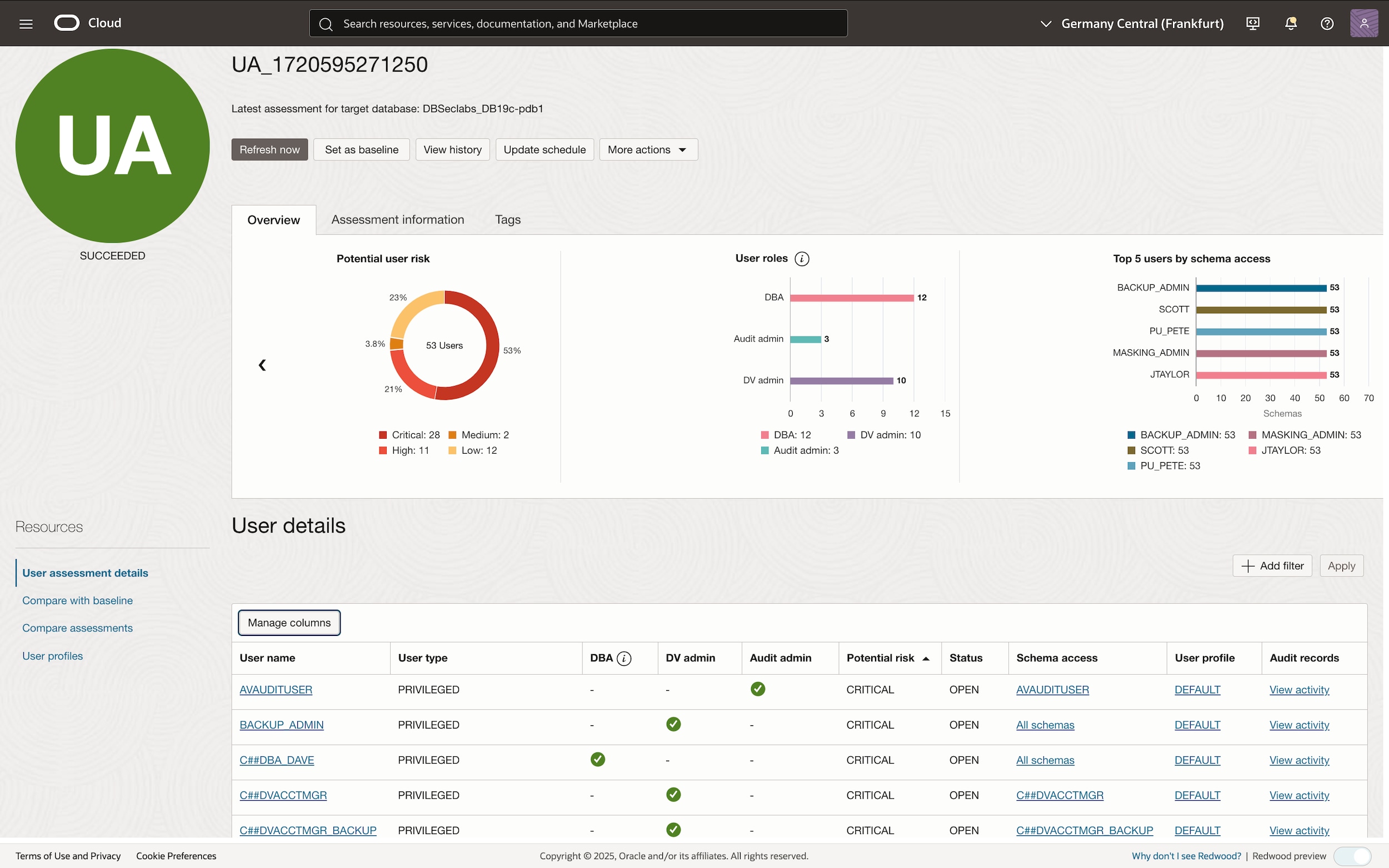
Privileged-user accounts are often soft targets for hackers attempting to gain access to critical systems and data. Continuous privileged-user activity monitoring allows security teams to easily identify anomalous behavior and quickly detect sensitive data leaks. To monitor privileged-user activity, first identify the privileged users in your system.
Identify privileged users
You can identify privileged database user accounts from different sources, such as the following:
- User Assessment report in Oracle Data Safe (shown on the left)
- Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool (DBSAT) report
- Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall (AVDF)
Audit privileged users
Top-level statements by administrative users, such as SYSDBA and SYSKM, are mandatorily audited when the database is in the closed or mount state. To audit the administrative user activity once the database is open, set up the following audits:
- Monitor all user-initiated activities of privileged administrators, including SYS.
- Monitor direct access to the database.
- Monitor all user-initiated activities of individual high-risk database accounts that have broad system access or access to sensitive data.
Audit security-relevant events
Security-relevant events are actions within the database that warrant greater scrutiny and constant monitoring because they can potentially be abused. Monitoring such actions helps detect anomalous activities in the database. These actions include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Any changes in the database-wide security policies using alter database/alter system.
- Events related to users, roles, privileges, grants, and revokes that alter access to the database.
- Database schema structure modification events.
- Activities using system privileges.
- Suspicious activities, such as multiple failed login attempts, sudden activity in dormant accounts, or non-business-hour operation.
Most of the security-relevant events can be audited using predefined audit policies. Refer to the Predefined audit policies for more details.
Audit access to sensitive data
Sensitive data access auditing is a powerful monitoring mechanism providing visibility into access and changes to sensitive data. It can serve as a primary deterrence to those who do not have a business reason to access or modify your data. Knowing your sensitive data landscape helps build focused audit policies to track its access.
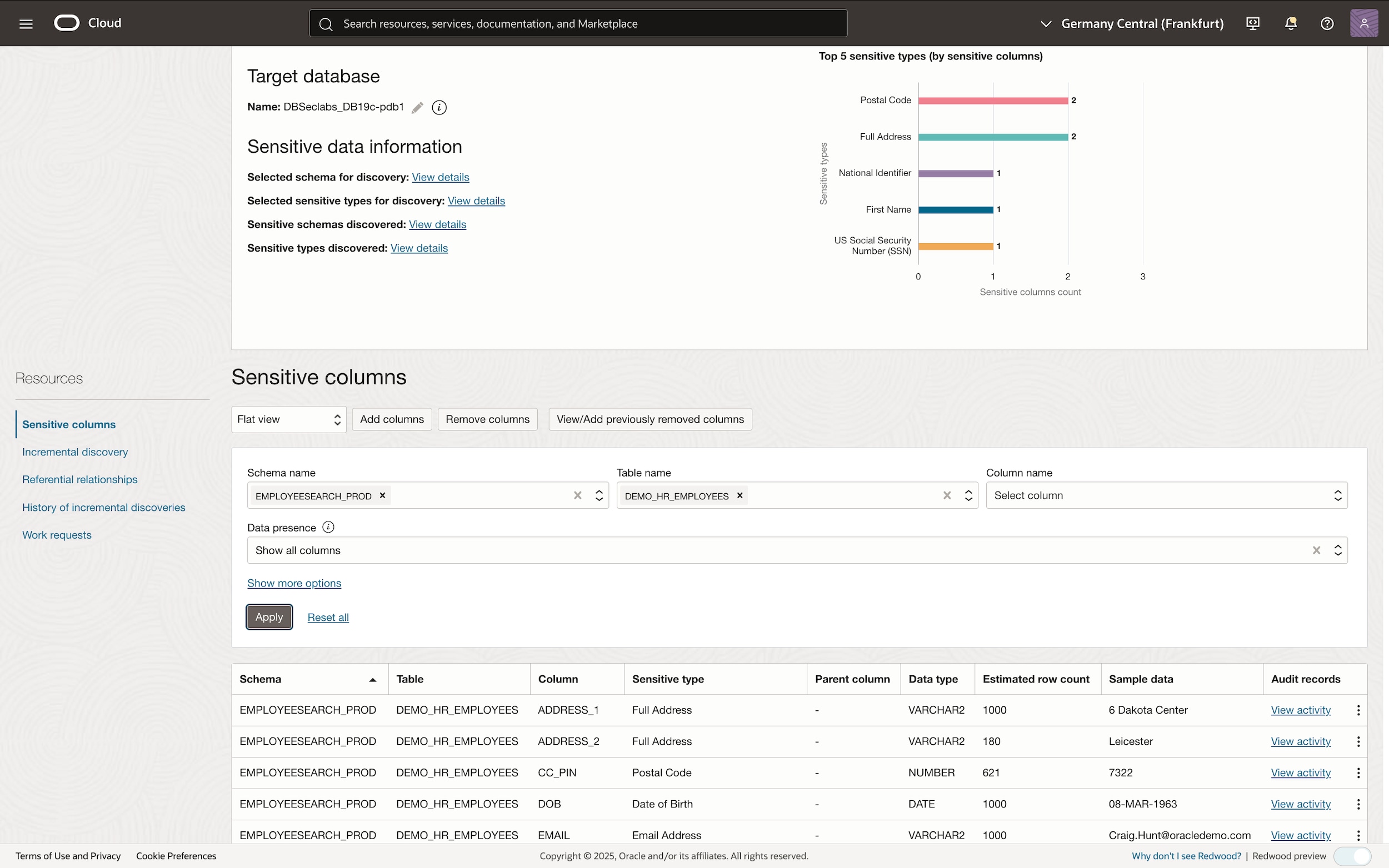
Identify your sensitive data landscape
Leverage one of the several sensitive data discovery tools, such as Data Safe, DBSAT, AVDF or Oracle Enterprise Manager to identify sensitive tables and columns, as shown on the left.
Audit sensitive data access
Once you understand your sensitive data landscape, you should determine who can access your sensitive data and audit their access.
- Monitor all access from outside the trusted path—even by authorized database users with a valid business reason, such as application service accounts—because it presents a higher risk.
- Monitor all access by database users who are authorized to interact directly with data.
- Audit all attempts by anyone else to access sensitive data as this presents the highest level of risk.
- Monitor access to sensitive columns storing personally identifiable information (PII) data.
Additional resources
-
Technical report
Get started with Unified Auditing
Run the Unified Auditing workshop
Get started on Unified Auditing key use cases in Oracle LiveLabs.
Try the Database Security Assessment Tool
Quickly assess database security posture and get recommendations to mitigate risks.
Contact sales
Talk to a team member about Oracle database security.