What Is an Autonomous Database?
Jeffrey Erickson | Senior Writer | August 15, 2025

Before a database can log transactions or support analytics, it must be set up, tuned, backed up, and patched, and the data it contains must be secured. These are all time-consuming jobs that require a deep understanding of database technology. Now, AI is taking on these tasks—and changing data management in the process. Let’s explore.
What Is an Autonomous Database?
An autonomous database is a fully managed cloud database that automates tasks traditionally performed by database administrators, or DBAs. These tasks include routine functions such as database tuning, backups, and updates, as well as security-based functions such as data encryption.
The automation inherent in these databases helps avoid problems caused by human error. In addition, the time and effort saved allows DBAs to apply their expertise to other functions, such as improving application functionality and providing AI models with the data architectures they need to perform optimally. Another top benefit of an autonomous database is that it can be quickly provisioned by users who need secure access to data—such as app developers, business analysts, or data scientists—without the help of a DBA.
Key Takeaways
- An autonomous database is a cloud native data management platform that can deploy, tune, and patch itself and manage security measures with no human intervention.
- Autonomous databases come in two flavors: one tuned for transactions and batch analytics, and one tuned specifically for data warehousing.
- Besides freeing database administrators from mundane, time-consuming tasks, an autonomous database can reduce the risk of errors.
Autonomous Database Defined
An autonomous database is a cloud database that uses AI to automate tuning, security, backups, updates, and other routine management activities traditionally handled by DBAs. Unlike a conventional database, an autonomous database can perform all these tasks and more without human intervention. That’s why these databases are often described as self-managing.
By automating a wide range of tasks, autonomous databases can help reduce operational costs, lower the risk of errors, and better mitigate security vulnerabilities.
Why Use an Autonomous Database?
Databases store critical business information and are essential for efficient operations in most organizations. Yet the DBAs who manage them are often overburdened with time-consuming manual tasks. These workload demands can lead to errors, which may have negative—even catastrophic—effects on uptime, performance, and security.
For example, failing to apply a patch correctly may weaken or altogether eliminate security protections, leaving an enterprise at risk for breaches that can result in serious financial and reputational damage.
The growing complexity of database management operations reveals another key benefit of an autonomous database. A single AI-driven application might require relational data and JSON data from business applications, as well as vector and graph data for semantic search operation. An autonomous database simplifies the data architecture needed to manage this complexity.
In addition, an autonomous database can scale up or down as needed to accommodate growing transaction and data warehouse demand, as well as AI training workloads that may have massive data sets. By automating the deployment, scaling, and optimization of database operations, an autonomous database helps teams overcome these challenges, opening the door to faster development and allowing data experts to focus on more high-value tasks.
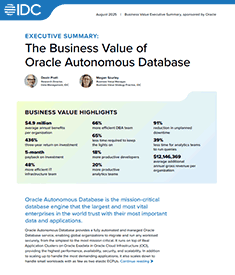
Companies using Oracle Autonomous Database gain benefits worth an average of $4.9 million per organization annually and realize a three-year ROI of 436%, says IDC.
How an Autonomous Database Works
An autonomous database provides full, end-to-end automation for provisioning, security, updates, high availability, performance, change management, and error prevention. To accomplish this, an autonomous database has specific characteristics.
- It is self-managing: All database and infrastructure management, monitoring, and tuning processes are automated. DBAs can now focus on other tasks, including data aggregation, modeling, processing, governance strategies, and helping developers use in-database features and functions.
- It is self-securing: Built-in capabilities help protect the database against both external attacks and malicious internal users. This helps mitigate concerns about cyberattacks on unpatched or unencrypted databases.
- It is self-repairing: These features work to minimize downtime, including unplanned maintenance. An autonomous database can require fewer than 2.5 minutes of downtime per month, even accounting for patching.
Benefits of an Autonomous Database
The benefits an organization can realize from an autonomous database depend on how teams use the system. A large company might use it to consolidate many disparate data sources into an easier-to-manage database, while a small business might use it as a scalable enterprise database that doesn’t need a large IT staff to maintain. Other potential benefits include:
- Database uptime: With automatic patching and security fixes, an autonomous database helps avoid the downtime that’s often required to make these necessary updates.
- IT efficiency: Managing a wide range of tasks through automation can eliminate many time-consuming manual tasks and minimize the risk of human error.
- Business productivity: When app developers, business analysts, and data scientists, and other users can manage the database lifecycle without waiting on IT, everyone becomes more productive.
- Cost reduction: An autonomous database lets DBAs manage more databases in the same amount of time, enabling them to devote more attention to higher-level tasks such as data modeling and applying their SQL programming expertise to improve application performance.
Key Features of an Autonomous Database
Because an autonomous database is a cloud-based database service, and since AI is what allows for automation of many traditional database administration tasks, IT teams should look at a few key features when selecting a system.
- Auto-provisioning: A core benefit of autonomy is the ability to deploy mission-critical databases without getting a DBA involved. For example, a developer can quickly deploy a database that enables scale-out protection in case of a server failure and allows updates to be applied in a rolling fashion while apps continue to run.
- Auto-configuration: The ability to automatically configure the database to optimize for specific workloads is also critical. When memory configuration, data formats, access structures, and other elements are optimized to improve performance, customers can simply load data and go.
- Auto-indexing: This feature automatically monitors workloads and detects missing indexes that could hinder applications. The database validates each index before implementing it and uses machine learning to learn from its own mistakes and improve.
- Autoscaling: This capability automatically scales compute resources as needed by workloads, enabling true pay per use. All scaling occurs online while the application continues to run.
- Automated data protection: An autonomous database can automatically protect sensitive and regulated data, assess the security of a configuration, and monitor for unusual activity.
- Automated security: Automatic encryption for the entire database, backups, and all network connections is crucial. Disallowing access to the operating system and restricting administrator privileges can help prevent phishing attacks and protect the system from both cloud infiltration and malicious internal users.
- Auto-backups: Do you need automatic daily backups, or backups on demand? The system should restore or recover a database up to any specified point in time within the last 60 days.
- Auto-patching: Gain the ability to automatically apply patches or upgrades with zero downtime. Applications continue to run as patching occurs in a round-robin fashion across clusters of nodes or servers.
- Automated fault detection and resolution: Using pattern recognition, hardware failures can be automatically predicted without long timeouts. I/Os are immediately redirected around unhealthy devices to avoid database hangs. Continuous monitoring for each database automatically generates service requests for any deviation.
- Automatic failover: Automatic failover with zero data loss to a standby database helps ensure that applications remain accessible and no data is lost, even if the primary database instance becomes unavailable. The process should be completely transparent to your applications and backed by a 99.995% SLA.
Types of Data Stored and Managed In an Autonomous Database
Information stored in a database management system can be either highly structured, such as accounting records or customer information, or unstructured, like digital image, audio, or email files. Data may be accessed directly by analysts or data scientists, or by customers and employees via enterprise software, websites, or mobile apps. More specifically, different applications use data in different formats—also known as data types. While in the past you might have used separate databases that specialize in each data type, an autonomous database can be set up to handle them all.
Common examples of data types include:
- Relational data is stored in rows and columns and organized into tables. This is the kind of data most frequently used in business applications, such as ERP or CRM systems, and for both transactions and data analytics.
- Document data is easily readable by both machines and application developers and is prevalent in highly scalable web applications. The most common document data format is the JSON file.
- Graph data is stored and indexed in a way that makes it easy to detect the distance and relationships between data points. Graph data is popular for mapping and data analytics applications. It’s also increasingly used alongside vector data to improve the accuracy of semantic search.
- Vector data is an AI calculation that represents the features of a digital object, such as a word, a sentence, a document, an image, or a video or audio file. Vectors are often stored and indexed in a vector database that helps computers search unstructured data by feature or semantic meaning, rather than by pixels or key value matches. This is a cornerstone technology for large language models and other AI systems.
Workloads of an Autonomous Database
Autonomous databases are tuned to align with various workload types. Popular uses for autonomous databases include:
- Data warehouse: These systems perform numerous functions related to business intelligence activities using data that’s been prepared for analysis. An autonomous data warehouse can rapidly scan millions of rows and can be deployed in a matter of seconds.
- Transaction processing: An autonomous transaction processing database preconfigured for row formats, indexes, and data caching can increase the number of transactions that can be simultaneously managed.
- Storing document data: Data such as JSON can be stored in a NoSQL document database as single, self-contained documents that can be retrieved quickly and easily. An autonomous JSON database can offer the benefits of both the document and relational models.
Autonomous Database Use Cases
An autonomous database can be used to bring new levels of efficiency and scalability to any situation where a traditional cloud-based relational, document, graph, or vector database would be used. This includes delivering the tools required for a range of AI projects in one place.
Here are some real-world use cases:
- Improve the operation of a globally scalable SaaS application. An autonomous database can be used to expand the efficiency and scalability of industry applications that global manufacturers depend on.
- Limit the number databases maintained by a large organization. A scalable autonomous database can be used to consolidate data from a wide range of sources, helping even the largest enterprises use database automation to significantly reduce the time spent gathering, formatting, and visualizing information.
- Provide scalable analytics for a data-hungry startup. An autonomous database can help a health science startup handle the massive data set required to sequence genetic data and vastly shorten the time it takes to provide the information for a diagnosis.
- Improve AI-driven customer support and analysis. By storing data generated from user interactions with an AI agent chatbot, a safety equipment provider can allow the database to be queried with natural language prompts, speeding customer response times.
Intelligent Technologies Support Autonomous Databases
Several fundamental intelligent technologies support autonomous databases, enabling automation of mundane but important tasks such as routine maintenance, scaling, applying security fixes, and database tuning. For example, an autonomous database’s AI algorithms include query optimization, automatic memory management, and storage management to allow for complete self-tuning.
AI can help companies improve database security by analyzing reams of logged data and flagging outliers and anomalous patterns—hopefully before any intruders can do damage. AI can also automatically and continuously patch, tune, back up, and upgrade the database without manual intervention, all while the system is running. This automation minimizes the risk that either human error or malicious behavior will affect database operations or security.
In addition, autonomous databases can deliver the following capabilities:
- Easy scalability: A cloud-based database service can expand or reduce its compute and memory resources instantly and as needed. For example, a company could scale up from eight processing units for the database to 16 for its end-of-quarter operations, then scale back down to eight afterward. In fact, all compute resources could be shut down over the weekend to reduce costs and then be started up again on Monday morning.
- Effortless database patching: Many data breaches happen because of system vulnerabilities for which patches are available but not yet applied. An autonomous database can prevent this by automatically rolling out patches against the cloud servers in a sequence designed to not cause downtime.
- Integrated intelligence: An autonomous database integrates monitoring, management, and analytics capabilities that leverage AI techniques. The goal is to automate database tuning, prevent application outages, and harden security across the entire database application.
The Developer Advantage: Build Scalable and Secure Enterprise Applications
With an autonomous database, developers have many options for building scalable and secure enterprise applications using data housed in a fully managed environment. That process starts with a simple, cost-effective environment for developing and testing applications before deploying them to a full production environment. Autonomous databases are hosted in the cloud and no DBA is needed to spin up new instances, making this an attractive and highly affordable option. Developers can create as many databases as they need, all for a flat rate.
Developers, and other teams with ideas for applications, may also be able to access helpful features and built-in tools, such as a low-code application development environment and container images. These allow users to work offline, then clone and deploy instances in the cloud. Developers will also appreciate in-database AI and the native use of various data types including JSON, vectors, graphs, spatial, and relational data.
Accelerate App Innovation with Oracle
Looking to increase your app development velocity with one database that does it all? Oracle Autonomous Database is built for AI and can help your business build scalable AI-powered applications with any data type, using your choice of large language model. You can then deploy your applications in the cloud or your data center.
Your developers can easily use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) across proprietary documents in various formats for AI vector search. They can also harness integrated AI services to enhance applications with text and image analysis, speech recognition, or personalized recommendations.
In addition, Oracle Autonomous Database automatically translates natural language into database queries, enabling contextual conversations without custom coding or manual operations.
Autonomous Database can provide a single data platform to meet your company’s needs, rather than a collection of specialty databases that IT has to maintain. With Oracle, you can keep data architectures simple by using SQL, JSON documents, graph, geospatial, text, and vectors in a single database to rapidly build new features. In fact, Oracle even provides a popular environment for generating applications without writing code. Stay focused on developing vital applications using a database that helps improve uptime and data security through automated measures and continuous monitoring.
And keep in mind that, by automating the relentless cycle of patching, tuning, and updating, autonomous databases don’t eliminate the database administrator role. They elevate it. Freed from routine maintenance, your IT professionals can now focus their expertise on higher-value pursuits such as data architecture improvements, strategic analytics, and making data an engine of business growth and competitive advantage for your business.
An autonomous database is one factor in configuring your data infrastructure for an AI future. Learn what other steps forward-looking companies are taking now.
Autonomous Database FAQs
What are the benefits of autonomous databases in data management?
An autonomous database simplifies data management by bringing together AI, development interfaces, and many data types in one data management system. It also automates many mundane, time-consuming tasks, allowing database administrators to work on other data management operations such as data modeling or data analytics.
What is autonomous data management?Autonomous data management is a system that turns over many daily data management functions to AI. These functions include deploying, updating, patching, and tuning the database, which AI can handle with minimal human intervention.